Some thoughts (and code) around GObject-Introspection
6 September 2010
There is one single thing that is, in my opinion, generating a fair amount of hype and reinvigorated interest in the GNOME platform: GObject-Introspection (or “GI” to save some typing). In short, it works like this:
- Library developers add annotations to the documentation comments of functions.
- The GI support tools generate XML and compiled API metadata.
- You have a library to use that metadata at runtime.
The last thing is very interesting, especially the runtime usage of
metadata… because it enables dynamic language bindings. This means
that developers no longer have to build e.g. the Python bindings for
themselves but just annotating the source code! (Side note, they already
exist as PyGI PyGObject.) A direct implication of this is
that there is a single “glue module” for your favourite language, and
that all GI-capable libraries are available without having to build
any code. To make it clear, let me put it this way:

Definitely GI is somewhat that makes the platform even more awesome than before, because it will allow for having support for more languages to be used to write GNOME applications, and also bindings will not lag behind the libraries.
Being so awesome, I wanted to try it out. It has been some time since I do not use Lua, so I thought it would be interesting to write GI glue code for Lua, provided that writing extensions using its C API is dead simple. This way LuiGI was born and I invested about a total of eight hours to write ~1300 lines of code which allow for using some GI-aware libraries. The mandatory screenshot:
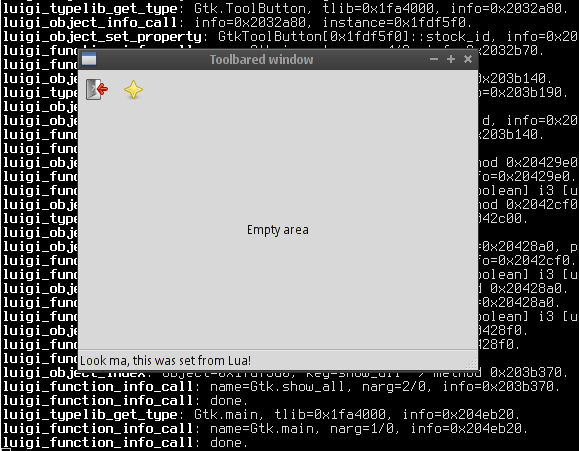
The above application window was created entirely from Lua, with LuiGI
using libgirepository to dynamically find functions, classes and
methods at runtime, using the following script (I especially like
how the Lua syntactic sugar for function calls on tables makes setting
properties at instantiation time look):
local Gtk = require ("gi").Gtk
Gtk.init (0, nil)
window = Gtk.Window { title = "Toolbared window",
default_width = 400,
default_height = 300,
allow_shrink = false }
sbar = Gtk.Statusbar { has_resize_grip = true }
toolbar = Gtk.Toolbar { tooltips = true }
vbox = Gtk.VBox {}
sbar_ctx = sbar:get_context_id ("default")
sbar:push (sbar_ctx, "Look ma, this was set from Lua!")
toolbar:insert (Gtk.ToolButton { stock_id = "gtk-quit" }, -1)
toolbar:insert (Gtk.ToolButton { stock_id = "gtk-about" }, -1)
vbox:pack_start (toolbar, false, false, 0)
vbox:pack_start (Gtk.Label { label = "Empty area" }, true, true, 0)
vbox:pack_end (sbar, false, false, 0)
window:add (vbox)
window:show_all ()
Gtk.main ()
Note that there is no event handling at all in the above code. The reason is that I have not implemented support for using Lua functions as callbacks.
What I think about GI after getting my hands dirty —by writing a bind,
no less— is that the Batman image above is perfectly well-grounded. The
code needed to glue GI support into some language is not trivial, but I
still think the API is quite convenient provided that it deals with a
rather complicated issue without breaking any existing GObject-based
code. The part I have found harder so far is handling conversion of
values between the Lua and C worlds.
Today I was hacking a bit more on LuiGI, and dropped by the
#introspection IRC channel, precisely to ask a couple of questions
about how to get some information for type conversion, and the kind
people there made me note about LGI, which is also a dynamic GI
binding for Lua. I have not been able of testing it because it needs a
bleeding edge libgirepository, but looking at its code I can tell that
it is more complete than my own, so I will be probably contributing to
it instead of duplicating efforts.
Some final words: I am truly convinced that GI does not only looks good, but it is actually very good. I foresee that this gust of fresh wind will bring more awesomeness to GNOME.